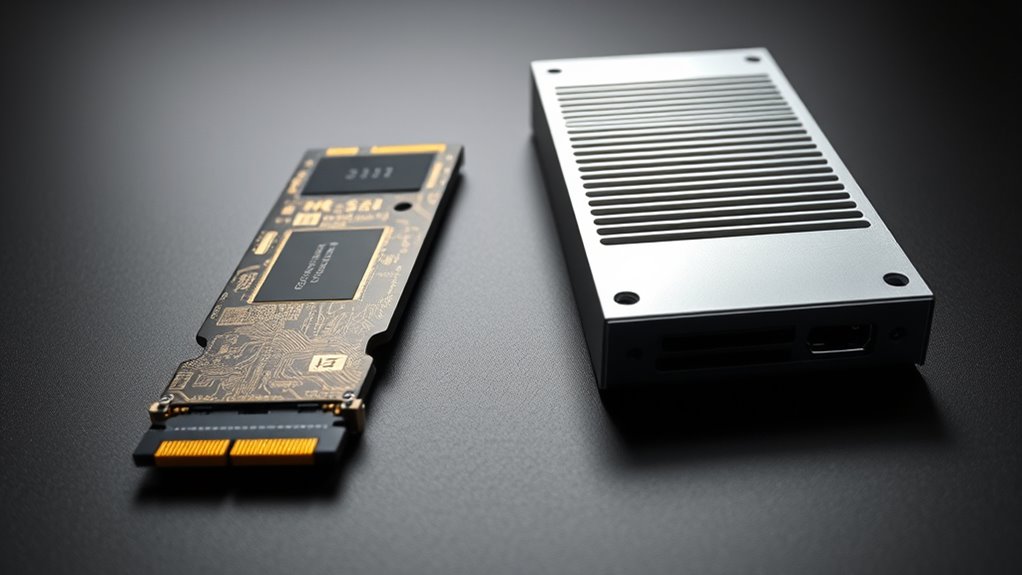
M.2 and SATA SSDs differ mainly in size, performance, and compatibility. M.2 drives are smaller, connect directly to the motherboard, and often offer faster speeds with NVMe technology, making them ideal for space-limited or high-performance setups. SATA SSDs are larger, use traditional cables, and provide reliable, budget-friendly storage for desktops and laptops. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right drive for your device and needs—more details are just ahead.
Key Takeaways
- M.2 SSDs are smaller, directly mounted on the motherboard, ideal for space-limited devices, while SATA SSDs are larger and installed in drive bays.
- NVMe M.2 drives offer significantly faster speeds (up to 3,500 MB/s) compared to SATA SSDs (up to 550 MB/s).
- M.2 supports PCIe and NVMe protocols, requiring compatible motherboards, whereas SATA SSDs use the standard SATA interface.
- M.2 drives generate more heat and need thermal management; SATA drives have better heat dissipation due to larger size.
- Choice impacts device compatibility, performance, power consumption, and system design, making the right selection crucial for optimal performance.
Overview of Form Factor and Size Differences

When comparing M.2 and 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, the most noticeable difference lies in their form factor and size. M.2 SSDs are compact, measuring about 22mm wide and 80mm long, resembling a thin stick of gum. They’re designed for space-constrained devices like ultrabooks, NUCs, and portable systems. In contrast, 2.5-inch SATA SSDs are larger, typically 100mm x 70mm x 7mm, fitting into standard drive bays in desktops and laptops. Their bigger size makes them less suitable for slim devices but easier to handle and install. The small, lightweight design of M.2 drives allows for internal mounting directly onto the motherboard, while 2.5-inch drives require external mounting with cables. This size difference influences compatibility, installation, and the device’s overall design. Additionally, thermal management considerations can vary significantly between these form factors, affecting performance and longevity. Proper heat dissipation strategies become especially important for high-performance M.2 drives due to their compact size, as compact design often limits airflow and cooling options. Furthermore, manufacturing standards ensure that both form factors meet specific performance and safety requirements, impacting their use cases.
Compatibility and Interface Options

M.2 SSDs offer a versatile range of interface options, allowing compatibility with different motherboard slots and systems. Depending on the drive and motherboard, you’ll find M.2 drives using either SATA or NVMe interfaces. M.2 SATA SSDs fit into B-keyed or M-keyed slots, but only work if the slot supports SATA connections. NVMe M.2 SSDs require an M-keyed slot with PCIe support. It’s important to check your motherboard’s specifications before purchasing. Compatibility also depends on the system’s motherboard configuration, as some systems may have limited M.2 slot support for certain interfaces. Additionally, verifying system BIOS settings can ensure proper recognition and optimal performance of your SSD. Ensuring correct installation procedures can prevent potential issues and maximize SSD lifespan. Meanwhile, 2.5-inch SATA SSDs use a standard SATA interface and connect via cables, making them compatible with most systems featuring SATA ports. The interface options directly influence compatibility, so understanding your system’s slot types and support guarantees you choose the right SSD type without issues. Furthermore, considering the storage capacity needs can help determine the most suitable SSD for your usage requirements. Additionally, verifying piercing care and hygiene practices can ensure your system remains free of infections that might impact overall performance.
Performance and Speed Capabilities

When comparing performance, you’ll notice that M.2 NVMe drives can reach transfer speeds up to 3,500 MB/s, far surpassing SATA-based options. Latency also drops with NVMe SSDs, leading to quicker response times in demanding tasks. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right drive for your speed-critical applications. Additionally, proper installation ensures you maximize these performance benefits and maintain safe operation. Selecting the appropriate interface type can further optimize your system’s overall speed and responsiveness. For optimal results, paying attention to compatibility considerations is essential to ensure your system fully leverages these advanced drives. Moreover, ensuring your system’s motherboard supports NVMe protocols is crucial for unlocking the full potential of these high-speed drives. Being aware of thermal management is important to prevent overheating and sustain peak performance during intensive use.
Data Transfer Rates
Data transfer rates are a key factor in determining the overall performance of SSDs, and the speed capabilities vary markedly between different types. With M.2 SATA SSDs, you’ll see speeds up to 550 MB/s, similar to traditional 2.5-inch SATA drives. In contrast, M.2 NVMe SSDs leverage PCIe lanes, delivering speeds of 3,500 MB/s or higher—way faster than SATA-based options. These higher speeds mean quicker file transfers, reduced load times, and better multitasking. Keep in mind, though, your motherboard’s support for NVMe or SATA influences what you can achieve. While SATA SSDs are limited by the SATA III cap, NVMe M.2 drives maximize the potential of PCIe, offering significant performance improvements in data transfer rates.
Latency Differences
While transfer speeds set the overall performance ceiling, latency plays a vital role in how quickly your SSD responds to data requests. Lower latency means faster access times, which considerably affects system responsiveness. NVMe M.2 SSDs have much lower latency compared to SATA SSDs because they use PCIe lanes, allowing rapid data transfer and quick command execution. SATA SSDs, limited by SATA III interfaces, experience higher latency due to slower data pathways. This difference impacts everyday tasks like booting, opening applications, or accessing files. Consider the table below:
| SSD Type | Typical Latency (ms) | Response Time (ns) |
|---|---|---|
| M.2 NVMe | 0.01 – 0.1 | 10 – 100 |
| M.2 SATA | 0.1 – 0.5 | 100 – 500 |
| 2.5-inch SATA | 0.1 – 0.5 | 100 – 500 |
Lower latency enhances overall system responsiveness. Additionally, latency differences can influence the perceived speed of your storage device in daily use.
Real-World Performance
Real-world performance differences between M.2 and SATA SSDs become evident in everyday tasks such as boot times, file transfers, and application loading. M.2 NVMe drives, with their higher speeds—up to 3,500 MB/s—significantly cut boot times and reduce wait times when opening large files or launching demanding programs. SATA SSDs, capped at 550-600 MB/s, still offer noticeable improvements over traditional HDDs but feel slower during intensive tasks. You’ll notice faster data transfers and smoother multitasking with NVMe M.2 drives, especially in modern systems supporting PCIe. Conversely, SATA SSDs provide reliable performance at a more affordable price, making them suitable for upgrades in systems lacking M.2 slots. The choice impacts your daily workflow, especially if speed is a priority.
Installation Processes and Use Cases

Installing M.2 SSDs is straightforward because they mount directly onto the motherboard’s M.2 slot, eliminating the need for cables. You simply insert the drive at an angle, then secure it with a screw. This process requires no extra tools beyond a screwdriver and is quick to complete. M.2 SSDs are ideal for compact and portable systems like ultrabooks, NUCs, and custom builds where space is limited. Conversely, 2.5-inch SATA SSDs need to be connected via SATA data and power cables and installed into drive bays within desktops or external enclosures. They’re better suited for traditional desktop setups or external storage solutions, where ease of installation and compatibility with existing drive bays matter most. Both types serve different use cases based on system design and performance needs.
Physical Durability and Handling

M.2 SSDs are resistant to minor shocks but can be damaged by significant drops. Their slim profile makes them less susceptible to physical bending. They lack external casing, increasing vulnerability to static and dust. Proper installation ensures secure connection and minimizes movement, reducing damage risk. Additionally, ventilation considerations are important to prevent overheating during operation. While lightweight and compact, handling M.2 drives carefully is essential to maintaining their longevity. They’re suitable for portable use but require gentle treatment to avoid damage, especially considering their durability limitations and the absence of protective casing, which can cushion impacts. Proper installation practices can also help mitigate some risks associated with handling. Being aware of handling techniques can further extend the lifespan of these drives and prevent accidental damage during installation or transport.
Power Consumption and Heat Management
You’ll notice that M.2 SSDs tend to use less power than 2.5-inch SATA drives, which can extend your device’s battery life. However, their compact size can lead to higher heat generation, requiring better cooling solutions. Proper thermal management is essential to maintain performance and prevent overheating. Additionally, the power efficiency of M.2 drives makes them a popular choice for portable devices and laptops. As thermal dissipation becomes increasingly important in high-performance SSDs, selecting drives with effective cooling features can help optimize their lifespan and reliability. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right drive based on power efficiency and thermal management needs.
Power Efficiency Differences
While both M.2 and 2.5-inch SATA SSDs are designed for efficient storage, they differ considerably in power consumption and heat management. M.2 SSDs typically consume less power, extending battery life in portable devices. However, their compact design often results in higher heat output, requiring better heat dissipation strategies. Conversely, 2.5-inch SATA SSDs draw more power but dissipate heat more effectively due to their larger surface area. Here are four key points:
- M.2 SSDs prioritize low power use, ideal for battery-powered systems.
- 2.5-inch SATA SSDs have higher power demands but better heat dissipation.
- Power efficiency in M.2 drives supports longer device runtimes.
- Heat management varies based on form factor, influencing performance and longevity.
Heat Generation Levels
Power consumption directly impacts heat generation in SSDs, affecting both performance and longevity. M.2 SSDs typically use less power than 2.5-inch SATA drives, mainly because of their smaller size and integrated components. However, because M.2 drives are more compact, they can generate more heat in a confined space, especially during intensive tasks like large file transfers or gaming. 2.5-inch SATA SSDs tend to dissipate heat more effectively due to their larger surface area, which helps spread out heat. While M.2 SSDs may run hotter, their lower power consumption reduces overall thermal stress, potentially extending lifespan. Proper heat management is essential to prevent overheating, which can throttle performance and shorten the drive’s durability over time.
Cooling Requirements
Because M.2 SSDs consume less power than 2.5-inch SATA drives, they generate less heat during typical operation. This reduces the need for extensive cooling solutions, making them ideal for compact systems. However, their high-density design can cause localized heat buildup, requiring proper airflow. Consider these points:
- Use heatsinks or thermal pads to manage heat in high-performance M.2 NVMe drives.
- Guarantee adequate airflow in small form-factor devices to prevent thermal throttling.
- Keep the drive environment cool, especially in laptops and mini PCs.
- Monitor temperatures regularly to avoid overheating and maintain ideal performance.
Practical Implications for Different Devices

Choosing between M.2 and 2.5-inch SATA SSDs depends heavily on your device type and use case. If you have a compact laptop, ultrabook, or mini PC, an M.2 SSD is ideal because it installs directly onto the motherboard, saving space and reducing clutter. For desktops with available drive bays, a 2.5-inch SATA SSD provides easy installation and compatibility. Portable external drives often utilize 2.5-inch SATA SSDs for durability and robustness, especially if they have sturdy enclosures. If speed matters, opt for NVMe M.2 drives, but ensure your device supports PCIe. For more basic needs or budget builds, SATA SSDs—even in 2.5-inch form—offer a reliable upgrade without complex installation. Your device’s physical constraints and performance goals should guide your choice.
Choosing the Right SSD for Your Needs

Selecting the right SSD depends on your device’s specifications, performance needs, and budget. To make an informed choice, consider these factors:
- Device Compatibility: Check if your system supports M.2 NVMe, M.2 SATA, or 2.5-inch SATA drives.
- Performance Requirements: For faster load times and high IOPS, choose NVMe M.2 SSDs. For general use, SATA options suffice.
- Form Factor: Opt for M.2 SSDs if space is limited, especially in ultrabooks or mini PCs. Choose 2.5-inch drives for desktops or external enclosures.
- Budget: M.2 NVMe SSDs tend to be pricier but offer better performance. SATA SSDs are more affordable and still considerably faster than traditional HDDs.
Align these factors with your specific needs for ideal performance and value.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can M.2 SSDS Be Used Externally Like Portable Drives?
You can’t directly use M.2 SSDs as external drives because they’re designed to fit into your motherboard’s M.2 slot. However, you can buy an M.2 to USB or SATA enclosure, turning your M.2 into a portable external drive. Just make sure the enclosure supports your M.2 type (SATA or NVMe). This way, you can enjoy fast speeds and easy portability, just like with traditional external SSDs.
Are All M.2 SSDS Compatible With All Motherboards?
You can’t just plug any M.2 SSD into any motherboard like a universal key. Compatibility depends on the M.2 slot type, supporting either SATA or NVMe interfaces, and the keying (B, M, or B+M). Picture a puzzle piece fitting perfectly; if your motherboard’s slot doesn’t match the SSD’s key or interface, it won’t work. Always check your motherboard’s specifications before choosing an M.2 drive.
Which SSD Type Offers Better Value for Gaming PCS?
For gaming PCs, NVMe M.2 SSDs offer the best value because they deliver faster load times and smoother gameplay compared to SATA options. You get higher speeds, lower latency, and improved performance without needing extra cables. While more expensive upfront, their speed benefits make them a smarter choice for gaming. If you want top-tier performance, investing in an NVMe M.2 SSD is worth it, especially for demanding titles and future-proofing.
Do M.2 NVME Drives Degrade Faster Than SATA SSDS?
No, M.2 NVMe drives don’t degrade faster than SATA SSDs. They have similar lifespans, measured in terabytes written (TBW), because both use NAND flash memory. However, NVMe drives often handle higher workloads and perform more intensive tasks, which can wear out the memory faster over time. Still, with normal use, both types will last years before experiencing significant degradation. Proper usage and maintaining free space help prolong their lifespan.
How Do Heat Issues Affect SSD Performance Over Time?
Heat issues can considerably impact your SSD’s performance over time. When your drive gets too hot, it may throttle its speed to prevent damage, leading to slower data transfer rates. Prolonged high temperatures can also accelerate wear on its components, reducing lifespan and reliability. To maintain peak performance, make sure your SSD stays cool by providing proper airflow, avoiding excessive workload, and using cooling solutions if necessary.
Conclusion
Choosing between M.2 and SATA SSDs depends on your device demands and data desires. Remember, swift speeds, simple setups, and solid-state stability make M.2 a mighty choice for many modern machines. But if compatibility counts or budget bounds, SATA still serves reliably. So, weigh your needs wisely, and don’t forget — understanding the differences delivers smarter, swifter storage solutions, saving you time, trouble, and tech headaches down the road.









